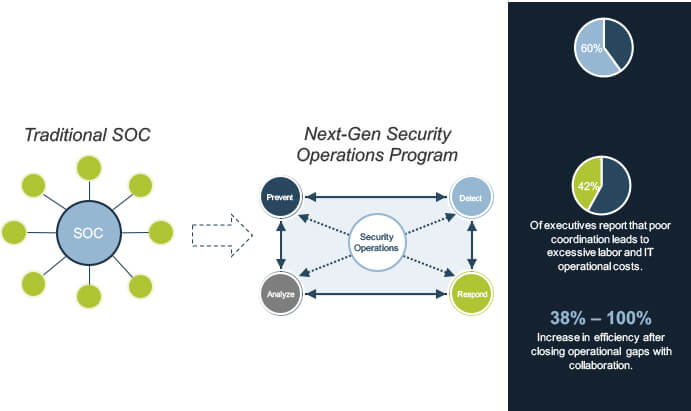
Transition from a Security Operations Center to a Threat Collaboration Environment.
“The evolution of the cyber threat landscape has forced organizations to think differently about security operations. Threat teams must actively collaborate in order to prevent, detect, analyze, and respond to cyber events with the potential to impact an organization’s brand, business operation, or technical infrastructure.” (TJ Minichillo, Senior Director, Security, Risk & Compliance)
Situation
- Organizations are struggling to defend against and prevent threats while juggling business, compliance, and consumer obligations.
- The increasing prevalence of public data breaches is highlighting the importance of proactive defensive measures.
- Threat management has become resource intensive, requiring continuous monitoring, collection, and analysis of massive volumes of security event data.
Complication
- There is an onslaught of security data – generating information in different formats, storing it in different places, and forwarding it to different locations.
- The organization lacks a dedicated enterprise security team. There is limited resourcing available to stand up or mature a security operations center.
- Many organizations are developing ad hoc security capabilities that result in operational inefficiencies, the misalignment of resources, and the misuse of their security technology investments.
- It is difficult to communicate the value of a security operations program when trying to secure organizational buy-in to gain the appropriate resourcing.
- There is limited communication between security functions due to a centralized security operations organizational structure.
Resolution
- A unified security operations process actively transforms security events and threat information into actionable intelligence, driving security prevention, detection, analysis, and response processes, addressing the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, and guiding continuous improvement.
Insight
1.Security operations is no longer a center, but a process. The need for a physical security hub has evolved into the virtual fusion of prevention, detection, analysis, and response efforts. When all four functions operate as a unified process, your organization will be able to proactively combat changes in the threat landscape.
2.Raw data without correlation is a waste of time, money, and effort. A SIEM on its own will not provide this contextualization. Prevention, detection, analysis, and response processes must contextualize threat data to supplement one another – true value will only be realized once all four functions operate as a unified process.
3.If you are not communicating, then you are not secure. Collaboration eliminates soiled decisions by connecting people, processes, and technologies. You leave less room for error, consume fewer resources, and improve operational efficiency with a transparent security operations process.
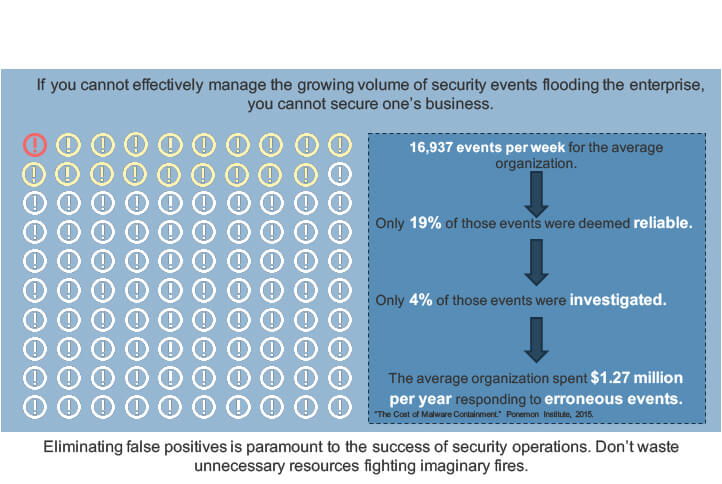
Data breaches are resulting in major costs across industries
Incident detection and escalation costs:
- Forensic and investigative activities, assessment and audit services, crisis team management and communications to executive management and board of directors.
Average cost is at an all-time high of $0.61 million per breach.
Notification costs:
- Creation of contact databases, determination of regulatory requirements, engagement of outside experts, postal expenses, secondary contacts to mail or email bounce-backs, and inbound communication set up.
Average cost was $0.56 million per breach.
Post data breach costs:
- Help desk activities, communications, investigative activities, remediation activities, legal costs, product discounts, identity protection services, and regulatory interventions.
Average cost increased to $1.64 million per breach.
Lost business costs:
- Abnormal turnover of customers, increased customer acquisition activities, reputation losses and diminished goodwill.
Average cost was $3.72 million per breach.
Traditional security operations centers are fragmented
Legacy security operations centers (SOCs) fail to address gaps between data sources, network controls, and human capital. There is limited visibility and collaboration between departments, resulting in siloed decisions that do not support the best interests of the organization at large.
Protect your organization with an interdependent and collaborative security operations program.
Common security operations challenges
- Organizational barriers separating prevention, detection, analysis, and response efforts. Siloed operations limits collaboration and internal knowledge sharing.
- Lack of knowledgeable security staff. Human capital is transferrable between roles & functions and must be cross-trained to wear multiple hats.
- Protecting everything. Avoid a shotgun approach. Prioritize and protect the assets that truly matter with the appropriate network controls. Doing so will also save unnecessary human capital costs
- Failure to evaluate and improve security operations. The effectiveness of operations must be frequently measured and (re)assessed through an iterative system of continuous improvement.
- Lack of standardization. Pre-established use cases and policies outlining tier 1 operational efforts will eliminate ad hoc remediation efforts and streamline operations.
- Failure to acknowledge the auditor as a customer.Many compliance & regulatory obligations require organizations to have comprehensive documentation of their security operations practices.
Benefits of an integrated operations process
Tactical Benefits
- Identifying threats earlier in the intrusion kill chain.
- Dynamic correlation and rule logic to improve the analysis process.
- Focused efforts on the most dangerous threats and vulnerabilities.
- Prioritized threat indicators to rapidly identify potential events.
Operational Benefits
- Improved situational awareness; data is provided with context, allowing security operations teams to shift their investigation from indicators to attackers’ tactics, tools, and procedures.
- Intelligence-driven security operational processes, reducing incident response times through the contextualization of incidents.
- Collaborative and unified prevention, detection, analysis, and response processes.
- Enhanced communication through the use of a central web/knowledge portal, defined escalation procedures, and a comprehensive ticketing function.
- A more intelligence-driven patch management process. Threat intelligence provides actionable vulnerability and exploitation data to identify critical vulnerabilities to patch.
- Standardized use cases that predefine the appropriate data collection, analysis, remediation and escalation protocol, reducing operational analysis efforts.
- Improved effectiveness of internal defense controls such as SIEM, NGFWs, IPS, IDS, SWGs, anti-malware and anti-spam packages.
- Increased operational efficiency in terms of asset and human capital management.
Strategic Benefits
- Improved organizational situational awareness; executives can understand relevant threats and appropriately allocate resources where necessary.
- Improved internal and external communication with top executives and board members about risks to the business, the probable actions of adversaries in the future, and the return on investments in security.
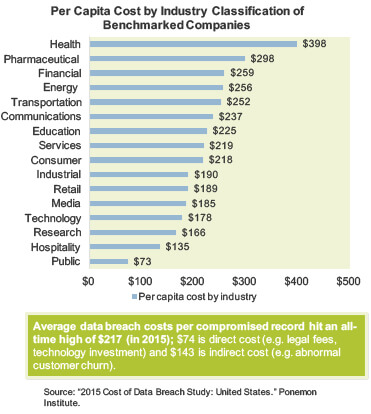
Effective security operations will improve capabilities and lower costs
Effective security operations management will help you do the following:
Improve efficiency
Effective security operations management practices develop structured processes to automate activities and increase process consistency across the IT organization.
Improve visibility and information sharing
Good operations management practices will expose weaknesses and potential problems to anticipate in the future and help security operations better prepare to move from a firefighting role to an innovator role. Good security operations management practices will also promote information sharing across different functions to enable good decision making.
Create and clarify accountability and responsibility
Security operations management practices will set a clear level of accountability throughout the IT organization, and ensure role responsibility for all tasks and processes involved in IT service delivery.
Control security costs
Security operations management is concerned with delivering promised services in the most efficient way possible. Good security operations management practices will provide insight into current costs across the organization and present opportunities for cost savings.
Identify opportunities for continuous improvement
Increased visibility into current performance levels and the ability to accurately identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
Improve threat protection
Stronger network controls through the hardening of perimeter defenses, an intelligence-driven analysis process, and a streamlined incident remediation process.
Metrics are merely the means to an action
Know your audience
Identify key stakeholders and understand what exactly they are expecting from the metrics.
Be S.M.A.R.T.
To provide practical value to your organization, metrics should be specific, measurable, attainable, repeatable, and time-dependent.
Data quality, validity, and confidentiality
The quality and validity of the data is key to driving meaningful metrics to your organization. In the meantime, you need to ensure the aggregated information should be accessed only by authorized people.
Standardize and automate the data collection process
To be consistent and effective, it might be better for your organization to standardize and automate the data collection process as much as you can.
Understand the cost of not having a suitable security operations program
One of the practical approaches to justifying the value of security operations is to identify the assets at risk and calculate the cost to the company should the information assets be compromised (i.e. assess the damage an attacker could do to the business).
Security controls | Technology investment: software, hardware, facility, and maintenance, etc. | $0-300K/year | $200K-2M/year |
| Security incidents
(if no security control is in place) | Explicit cost: 1) Incident response cost: • Remediation costs • Productivity: (number of employees impacted) × (hours out) × (burdened hourly rate) • Extra professional services • Equipment rental, travel expenses, etc. • Compliance fine • Cost of notifying clients 2) Revenue loss: Direct loss, the impact of permanent loss of data, lost future revenues 3) Financial performance: Credit rating, stock price Hidden cost:Reputation, customer loyalty, etc. | $15K-650K/year | $270K-11M/year |